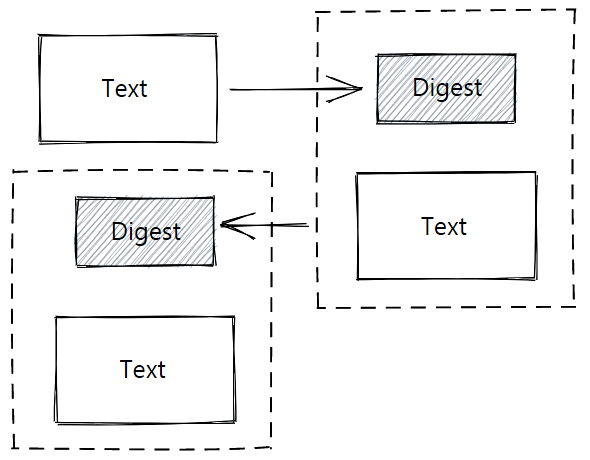
[This post is a note to self] – Blockchains are a type of ledger. Coin “miners” make calculations and add messages to the blockchain over time. The messages are hashed to protect the ordering and contents of messages. These hash ledgers are (allegedly!) tamper-resistant as the contents of later entries depend on the contents of earlier entries.
The novelty (in comparison to conventional dbs) is that it is a distributed system with no owner. This is what enthusiasts mean when they say that the blockchain is trustless: instead of central authority, like a bank, many miners compete to successfully write a new message to the blockchain. They do this by means of a proof-of-work algorithm, each with their own copy of the ledger.