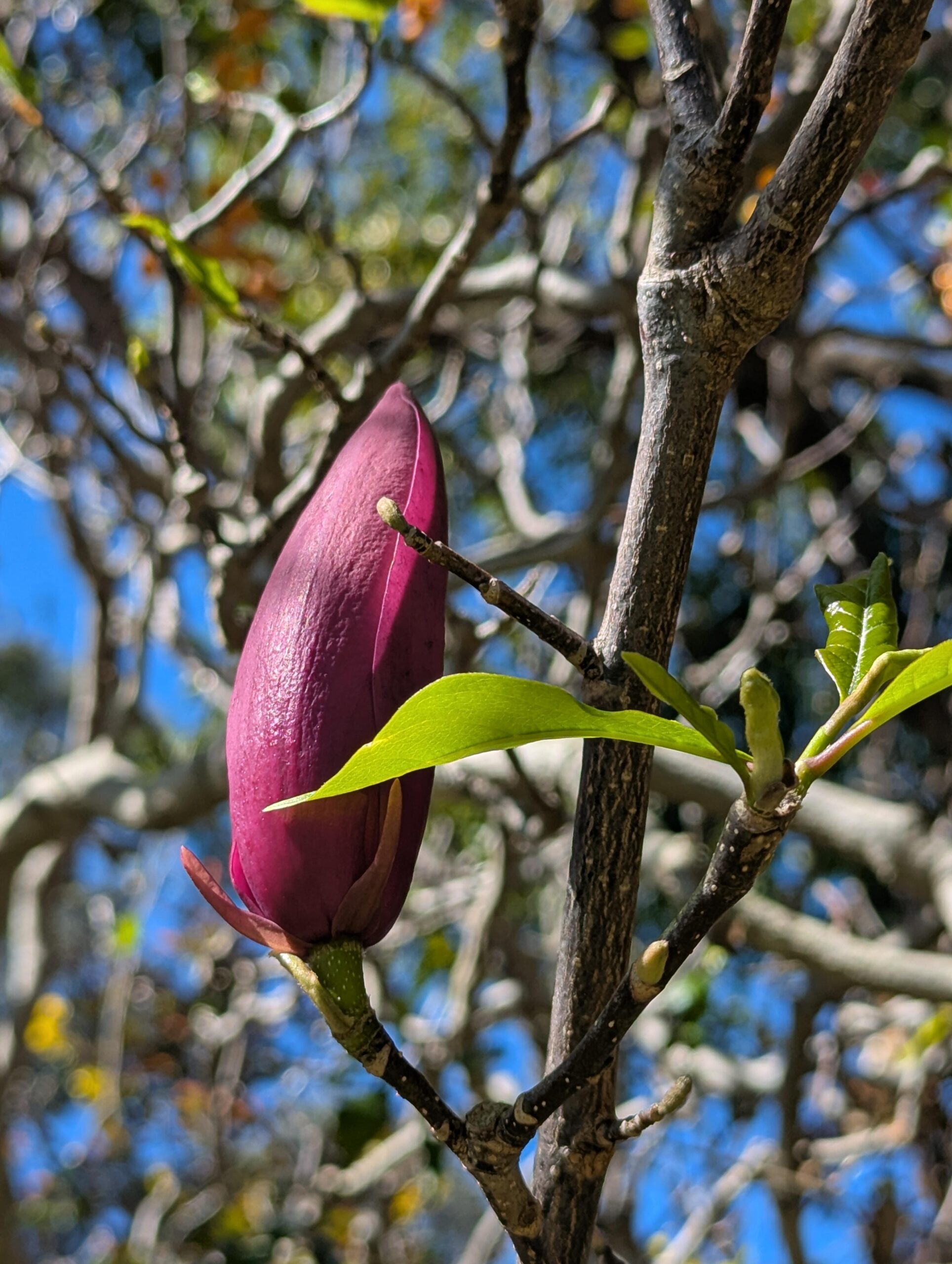
Magnolias are blooming all around

Environment & Biodiversity
Love this article <3 (because I love pebbles :D)
“During the ice-age when Australia was nearer the South Pole, glaciers dominated the landscape. As glaciers bulldozed through the landscape, rocks and debris were picked up and carried along in the weight and movement of ice. When the glacier reached the ocean, chunks carved off into icebergs. The stones frozen in the iceberg floated offshore.
As the iceberg melted, the stones dropped into the ocean. The glaciers pick up that material, move to the edge of the continent, then move out to sea with it, then drop it. That’s why Geologists call these stones dropstones, or ice rafted debris, and many such pebbles have washed up on the strip of coastline that includes Singing Stones Beach.”

https://www.abc.net.au/news/2024-07-31/epic-history-behind-famous-singing-stones-beach/104148526
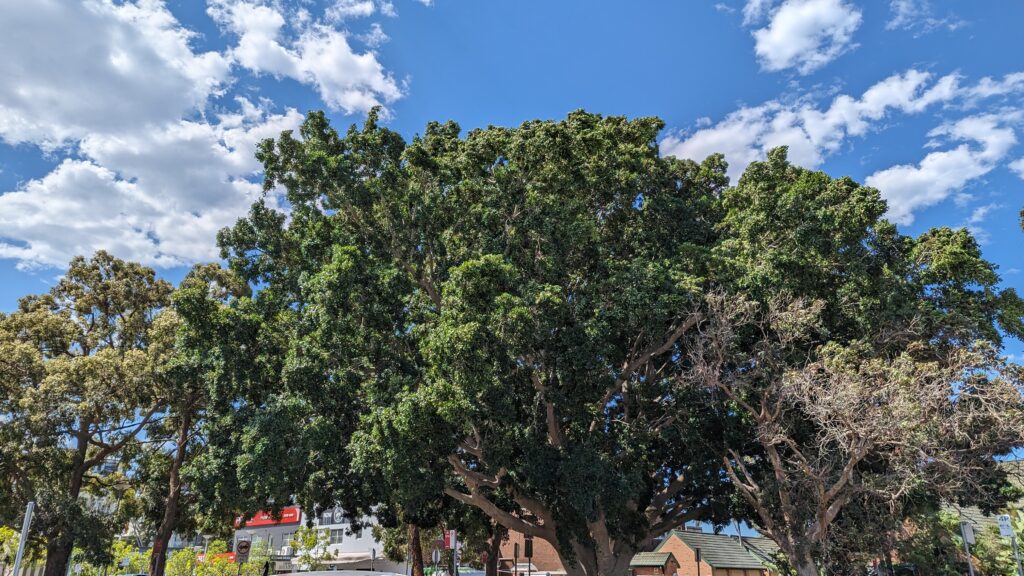
Please help save the fantastic fig tree outside my house o/`
Add your support here -> Change.org/p/save-the-significant-fig-tree-in-alfred-st-ramsgate-beach-sans-souci-nsw

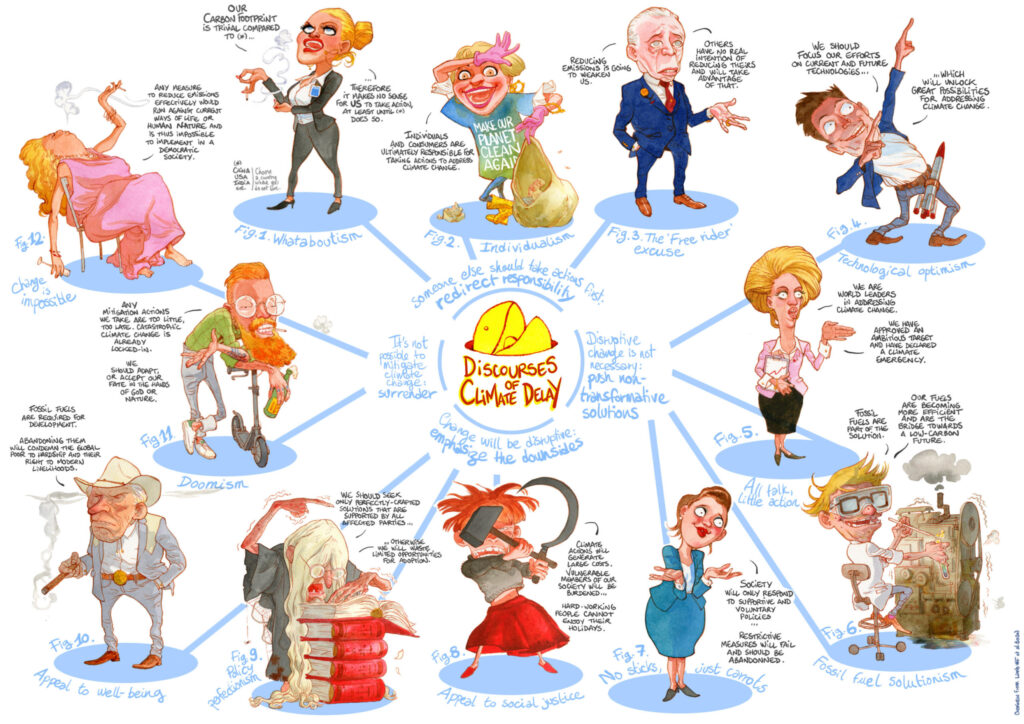
“Discourses of Climate Delay” – awesome work by Léonard Chemineau
All characters plus the printable version in several languages can be found at Leolinne.com/?portfolio=discourses-of-climate-delay
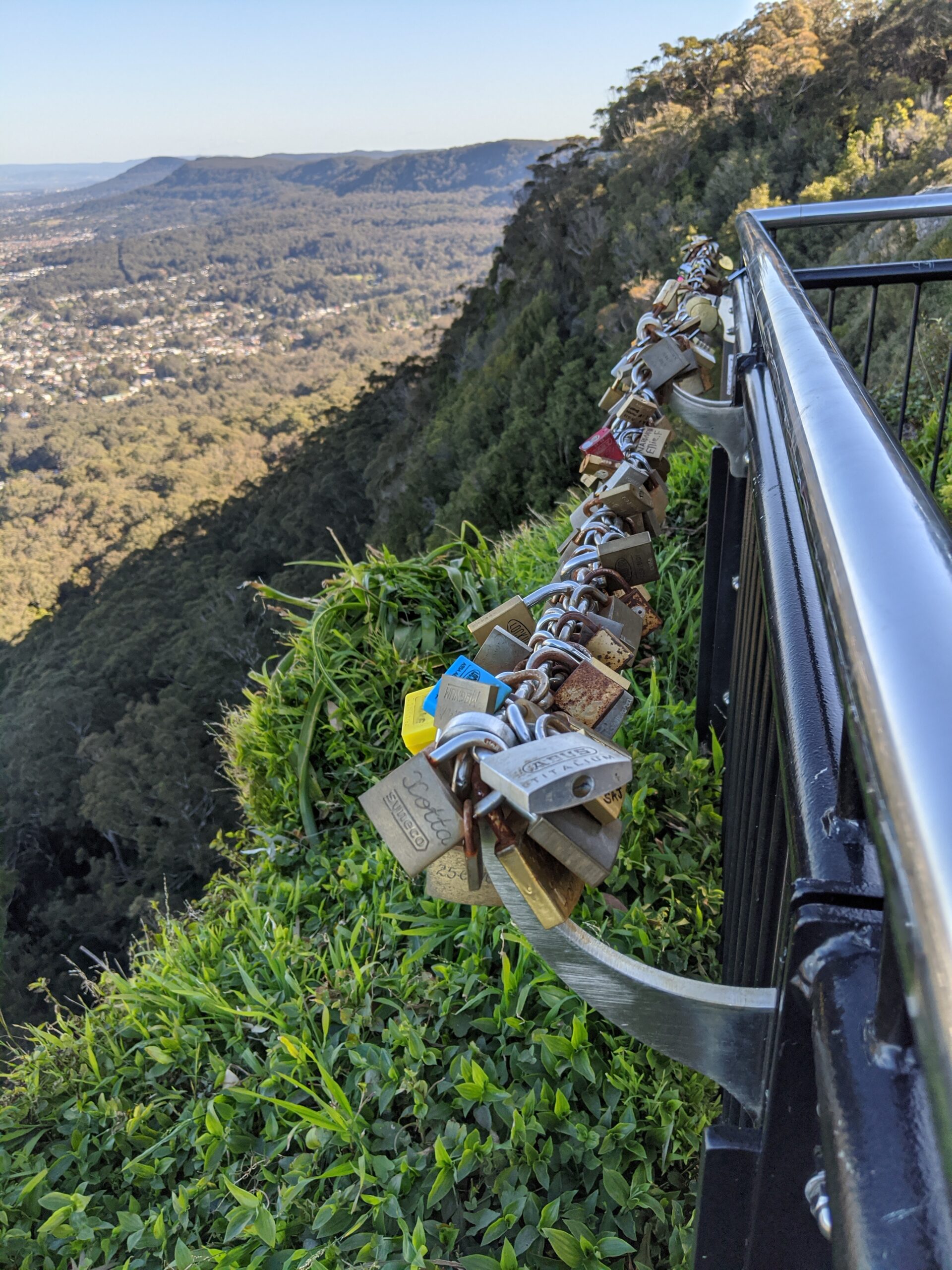
Recently I got caught up in a commentary to a tweet of mine where I expressed concerns over people leaving stuff behind in National Parks, like the locks people put on railings. The argument put forward was that people do that because they grieve, and then they can’t think of someone else’s concerns, and also if something is man-made anyone can attach something to it.
I disagreed, saying by that definition anyone can put anything anywhere at any time. The discussion stopped, days later I found myself blocked by that account.
While it is unpleasant to be excluded by someone at random, I still stand by my conviction that if we don’t take the care for our surroundings more serious at all times, none of the protection that we’re hoping to give to our natural world will work.
So does grief out-rule ecology? No, it does not.
Instead it could be used for its safeguard, not against it. One way to connect loss to a memorable element in nature is to plant a tree, or donate towards upgrading the National Park that was visited. There are plenty of ways to create a memory that is in sync with the aim of protecting our natural environment.
Loveliveson.com/memorial-trees-australia
Plantatreeforme.org.au

To my country, from an expat – Ben Lawson poem
The average Australian’s diet has a water scarcity footprint of 362 litres per day. A water scarcity footprint consists of two elements: the litres of water used, multiplied by a weighting depending on whether water scarcity at the source is higher or lower than the global average.
Foods with some of the highest water scarcity footprints were almonds (3,448 litres/kg), dried apricots (3,363 litres/kg) and breakfast cereal made from puffed rice (1,464 litres/kg).
In contrast, foods with some of the smallest water scarcity footprint included wholemeal bread (11.3 litres/kg), oats (23.4 litres/kg), and soaked chickpeas (5.9 litres/kg).
Of the 9,000 diets studied, 25 per cent of the water scarcity footprint came from discretionary foods and beverages such as cakes, biscuits, sugar-sweetened drinks and alcohol
Food systems account for about 70 per cent of global freshwater use.
Read the whole article here: https://www.abc.net.au/news/2019-10-07/chocolate-wine-food-production-water-use-climate-change/11578608